
This Mail Merge in Word tutorial is s uitable for users of Word 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and Word for Microsoft 365.
How to do a mail merge in word for nametags how to#
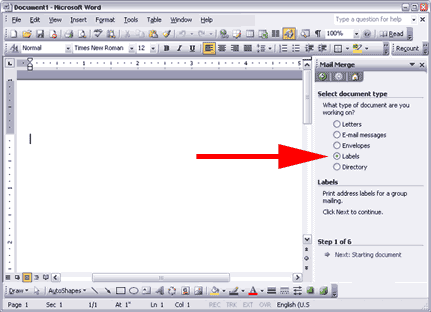
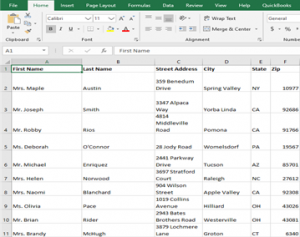
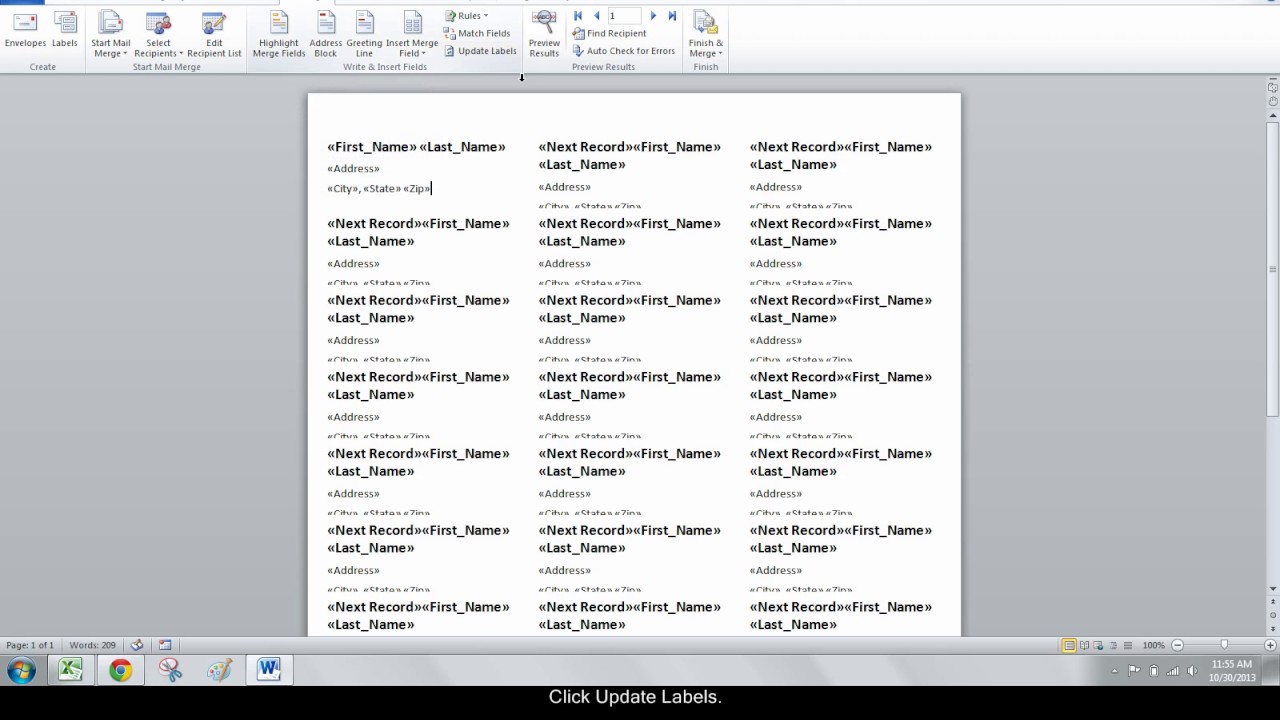
Home > Microsoft Word > How to Mail Merge in Word How to Mail Merge in Word
Therefore, the moment of inertia depends not only on the mass, shape, and size of the body but also the distribution of mass in the body about the axis of rotation. Therefore, the radius of gyration is the distance from the axis of a mass point whose mass is equal to the mass of the whole body and whose moment of inertia is equal to the moment of inertia of the body about the axis.

Notice that we can write I = M k 2 where k has the dimension of length. It is related to the moment of inertia and the total mass of the body. Radius of GyrationĪs a measure of the way in which the mass of a rotating rigid body is distributed with respect to the axis of rotation, we define a new parameter known as the radius of gyration. In simple words, moment of inertia is the measure of the way in which different parts of the body are distributed at different distances from the axis. On comparing equation II with the formula of the kinetic energy of the whole rotating body in linear motion, it is evident that mass in linear motion is analogous to the moment of inertia in rotational motion. We already know that linear velocity in linear motion is analogous to angular acceleration in rotational motion. It is the characteristic of the rigid body and the axis about which it rotates. The parameter I is independent of the magnitude of the angular velocity. Let Σ m i(r i ) 2 be I which is a new parameter characterising the rigid body known as the Moment of Inertia. Therefore, taking ω out of the sum, we get, We know that angular acceleration ω is the same for all particles. ∴ K = Σ k i = 1/2 ( Σ m i(r i ) 2ω 2 ) where n is the number of particles in the body. Where m i is the mass of the particle. The total kinetic energy K of the body is thus the sum of the kinetic energies of individual particles. What is the analogue of mass in rotational motion? To answer this question, we have to derive the equation of kinetic energy in rotational motion.Ĭonsider a particle of mass m at a distance from the axis with linear velocity = v i = r iω. Therefore, the kinetic energy of this particle is, ∴ Moment of inertia I = Σ m ir i 2 Kinetic Energy in Rotational Motion Formula for Moment of Inertia can be expressed as: Moment of inertia is the property of the body due to which it resists angular acceleration, which is the sum of the products of the mass of each particle in the body with the square of its distance from the axis of rotation. Each particle in the body moves in a circle with linear velocity, that is, each particle moves with an angular acceleration. In rotational motion, a body rotates about a fixed axis. So we have studied that inertia is basically mass. Because the heavier one has more mass, it resists change more, that is, it has more inertia. For instance, it is easier to throw a small stone farther than a heavier one. More the mass of a body more is the inertia. But what causes inertia in a body? Let’s find out. What is Inertia? It is the property of a body by virtue of which it resists change in its state of rest or motion.
Angular Velocity and Angular Acceleration.Theorems of Parallel and Perpendicular Axis.Browse more Topics Under System Of Particles And Rotational Dynamics Understand the Theorem of Parallel and Perpendicular Axis here in detail. Therefore, it gets pushed backward, that is, it resists change in its state. As soon as you board the moving train, your lower body comes in contact with the train but your upper body is still at rest. That is because before boarding the train you were at rest. Similarly, when you board a moving train, you experience a force that pushes you backward. Therefore, when the bus stopped, your lower body stopped with the bus but your upper body kept moving forward, that is, it resisted change in its state. Your lower body is in contact with the bus but your upper body is not in contact with the bus directly. When the bus stopped, your upper body moved forward whereas your lower body did not move. What did you experience at this point? Yes. After a few minutes, you arrive at a bus stop and the bus stops.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
